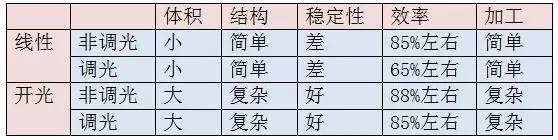
In terms of current wafer technology: wafer energy = 70% light + 30% heat. For a four filament A60 bulb, the filament power is about 4W, then at least 1.2W of heat is generated by 30% heat. It sounds like 1.2W is not much, but the loss of manpower and material resources caused by the dead lights can not be underestimated. The heat of the filament is to be dissipated, mainly through three ways: One is (conduction): wafer-bracket-wire-lamp part; The second is (convection): wafer-fluorescent gel-bubble gas-glass bulb-air; The third is (radiation): wafer - fluorescent glue - radiated to the air; As mentioned above, for LEDs, the radiation is small and can be ignored, focusing on conduction and convection. From the point of view of the heat path, it seems that it is not long, then whether this road can quickly conduct heat, you have to analyze it carefully: The wafer is a heat source, and the heat is constantly generated. The support is a carrier. At present, most commonly used brackets are made of ceramic and sapphire. The wires are made of metal, and the base of the lamp is considered to be hot. From the material point of view, it is basically heat conduction, but from the conduction formula, both the bracket and the cross section A of the wire are too small, which directly leads to the Q magnitude being too small, which is almost negligible. In addition, as a warm lamp head, the belly is hollow, just a layer of metal shell, and how much heat can be accepted! As a result, the effect of conduction in the heat dissipation of the filament lamp is minimal. Let's talk about convection: In order to travel fast in the tropics, the contact surface of "fluorescent glue - gas inside the bulb" must first be guaranteed. From the convection formula, the h value of static air is generally 3~10W/m^2*k, and the section A at this time is more than 1000 times of A in conduction (calculated according to the filament of the following figure), so that convection heat The Q value can also be on the order of watts. Under the push of the temperature difference, the air in the bulb quickly brings the heat on the filament to the bulb, which is then transferred to the air. Some people will say that glass is a poor conductor and heat transfer is very slow (this is true), but when the glass thickness is very thin and the contact area is increased, this poor conductor can also conduct heat very well (this is the same as the plastic aluminum principle). ). In summary, through analysis, we can draw the conclusion that the absolute main effect on the heat dissipation of the filament light source is convection! As we said before, the filament lamp has two heat sources, one light source and one power source. We have already discussed the light source section above. Below I discuss the heat dissipation of the power supply section: There are two types of filament lamps currently used most commonly: From the tabular data, at least 15% of the power is used to generate heat, and 5W is 0.75 watts. If this part of the heat treatment is not good, the life of the power supply is not guaranteed, and the probability of a problem rises linearly. However, at present, many manufacturers do not handle it, and it can be wrapped directly with insulating paper. Analysis of the current status of the filament, let's discuss, there is no way to improve heat dissipation: For the light source part, we already know that the convection plays a major role. What can increase the flow of gas in the blister? Some friends may already know - inflated! It is a more feasible way to fill in the active gas, which can significantly improve the flow of gas and provide the maximum power that the filament can do. This is also a process familiar to traditional light bulb factories. It is easy to use and has low investment. Many factories are doing this. For the power supply part, you want to reduce the temperature, especially the temperature of the electrolysis, by filling the glue or operating a simpler thermal mud. Through these methods, the cost will increase a little, but the effect is very obvious. It is indispensable to make products with good stability and long life. Regarding power supply noise and whether there is a better way to improve heat dissipation, we will share it next time.
Dongguan Deli Plastic Co.,Ltd is a manufacturer specialized in the research, development ,plastic injection mould and making mass production with well-equipped facilities and strong technical force.
Our products are extensively used in household industry/electronic industry/automobile industry/building industry and other industries.
Cute Fan,Cute Usb Fan,Cute Mini Handy Fan,Desktop Cute Small Fan Guangdong Aiyimi Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.nbminifan.com

We have rich experience on one-stop solution, provide various services from new product design,prototype,mold making,mass production,assembly and logistics. The most important advantage is we have our own R&D team to help clients to turn ideas into actual parts. All of these engineers and designers have over 15 years experience in these plastic products fields.
We have a strict quality control system, an excellent management team and also a dedicated sales force, enable us to fulfill our commitment in high quality products and outstanding services.
If you are looking for a trustworthy supplier of customized items, please do not hesitate to contact us. We are always striving to establish a win-win partnership with customers from all over the world and help our partners to stay one step in front of your competitors.